Biogas is a renewable energy source produced from the anaerobic digestion of organic materials such as agricultural waste, animal manure, municipal solid waste, or food scraps. It is primarily composed of methane (![]() ) and carbon dioxide (
) and carbon dioxide (![]() ), along with trace amounts of other gases like hydrogen sulfide (
), along with trace amounts of other gases like hydrogen sulfide (![]() ) and ammonia (
) and ammonia (![]() ). Biogas has become a key component in the transition to sustainable energy systems, offering a versatile range of uses in power generation, heating, transportation, and agriculture.
). Biogas has become a key component in the transition to sustainable energy systems, offering a versatile range of uses in power generation, heating, transportation, and agriculture.
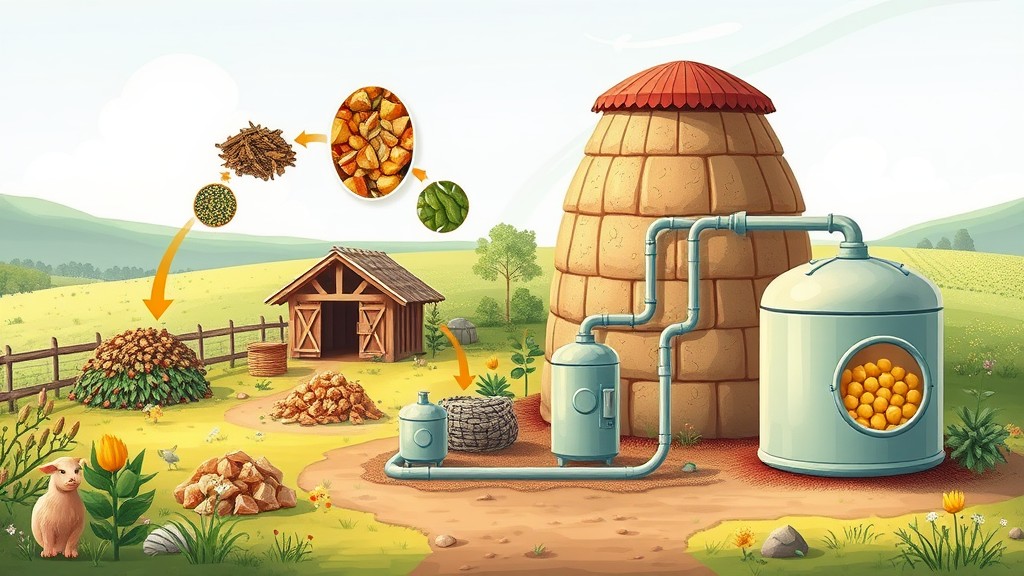

This article explores the various uses of biogas, highlighting its significance in promoting renewable energy, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and supporting sustainable waste management. Practical examples illustrate its role in modern energy systems and its potential to drive economic and environmental benefits.
What is Biogas?
Biogas is generated through the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms in the absence of oxygen. This process, known as anaerobic digestion, takes place in biogas plants or naturally in landfills. The main components of biogas, methane and carbon dioxide, give it its energy value and define its suitability for various applications.
The composition of biogas typically includes:
- Methane (
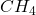 ): 50–70%
): 50–70% - Carbon dioxide (
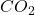 ): 30–50%
): 30–50% - Hydrogen sulfide (
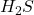 ): 0–3%
): 0–3% - Other trace gases
The energy content of biogas depends on its methane concentration, as methane is the combustible component that provides energy. Purified biogas, often referred to as biomethane, can be upgraded to a high methane content for more efficient use.
Uses of Biogas
Biogas is a highly flexible energy source with numerous applications across different sectors. Its uses range from generating electricity and heat to fueling vehicles and enriching soil in agriculture.
1. Electricity Generation
Biogas can be used to generate electricity in combined heat and power (CHP) systems or biogas power plants. The methane in biogas is burned in engines or turbines to produce electricity, making it a clean and renewable energy source.
How It Works:
- Biogas is fed into a gas engine or microturbine.
- The combustion of methane generates mechanical energy, which is converted into electricity.
Example: In Germany, biogas plants contribute significantly to the renewable energy grid, supplying electricity to thousands of households. A biogas plant processing manure and crop residues can generate electricity for a small village, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Benefits:
- Renewable and sustainable energy production.
- Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by capturing methane that would otherwise escape into the atmosphere.
- Diversification of energy sources, enhancing energy security.
2. Heating and Cooking
Biogas is widely used for heating and cooking in residential and industrial settings. Its clean-burning properties make it a more environmentally friendly alternative to conventional fuels like firewood, coal, or liquefied petroleum gas (LPG).
How It Works:
- Biogas is piped directly to stoves or heating systems.
- It burns efficiently, producing a consistent flame suitable for cooking or heating water.
Example: In rural India, biogas digesters are installed in households to convert cow dung into biogas for cooking. This reduces indoor air pollution caused by burning firewood and improves the quality of life for rural families.
Benefits:
- Provides a clean and affordable cooking fuel, especially in rural areas.
- Reduces deforestation by decreasing dependence on firewood.
- Minimizes exposure to harmful indoor air pollutants.
3. Transportation Fuel
When purified and upgraded to biomethane, biogas can be used as a renewable transportation fuel. Biomethane is chemically similar to compressed natural gas (CNG) and can power vehicles equipped with CNG-compatible engines.
How It Works:
- Raw biogas is purified to remove impurities like
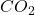 and
and 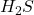 , leaving nearly pure methane.
, leaving nearly pure methane. - The biomethane is compressed and stored as CNG or liquefied as LNG for use in vehicles.
Example: In Sweden, city buses in Stockholm run on biomethane derived from food waste and sewage. This reduces the city’s carbon footprint and promotes a circular economy by repurposing organic waste into transportation fuel.
Benefits:
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to diesel or gasoline.
- Decreases reliance on non-renewable fossil fuels.
- Supports waste-to-energy initiatives, improving waste management.
4. Industrial Applications
Biogas is used in various industries to meet energy needs for processes like heating, steam generation, and drying. Its cost-effectiveness and renewable nature make it an attractive energy source for businesses.
How It Works:
- Biogas is burned in boilers to produce heat or steam, which is then used in manufacturing processes.
Example: The food processing industry often uses biogas generated from organic waste like fruit peels and food scraps to fuel boilers. This reduces energy costs and manages waste efficiently.
Benefits:
- Reduces energy costs for industries.
- Lowers waste disposal expenses.
- Contributes to corporate sustainability goals.
5. Fertilizer Production
The anaerobic digestion process that produces biogas also yields a nutrient-rich byproduct called digestate. Digestate is an excellent organic fertilizer that can be used to improve soil health and agricultural productivity.
How It Works:
- The digestate is separated into liquid and solid fractions.
- The liquid fraction is used as a liquid fertilizer, while the solid fraction is composted for use in farming.
Example: In agriculture, biogas plants process cow manure and crop residues, producing digestate that farmers use as a natural fertilizer. This reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and promotes sustainable farming practices.
Benefits:
- Enhances soil fertility and crop yield.
- Reduces reliance on synthetic fertilizers, which are energy-intensive to produce.
- Minimizes nutrient runoff, protecting water quality.
6. Waste Management
Biogas production offers an efficient solution for managing organic waste from households, agriculture, and industries. By converting waste into energy, biogas plants reduce the volume of waste that would otherwise end up in landfills or incinerators.
How It Works:
- Organic waste is collected and fed into anaerobic digesters.
- The resulting biogas is used for energy, while the digestate is used as fertilizer.
Example: Municipalities in countries like the Netherlands use biogas plants to process organic waste from households and restaurants. This reduces landfill volumes and generates electricity for local use.
Benefits:
- Diverts organic waste from landfills, reducing methane emissions.
- Provides a sustainable waste disposal method.
- Supports circular economy principles by turning waste into valuable resources.
7. Greenhouse Gas Reduction
Biogas helps mitigate climate change by capturing methane emissions from organic waste and utilizing them as an energy source. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, and its capture significantly reduces its impact on global warming.
How It Works:
- Biogas systems capture methane released during the decomposition of organic waste.
- The captured methane is converted into energy, preventing its release into the atmosphere.
Example: Landfill gas recovery projects in the United States collect methane from landfills and convert it into electricity or heat. These projects prevent millions of metric tons of ![]() -equivalent emissions annually.
-equivalent emissions annually.
Benefits:
- Reduces methane emissions, which are 25 times more potent than
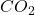 in causing global warming.
in causing global warming. - Promotes sustainable waste management.
- Aligns with international climate goals, such as those outlined in the Paris Agreement.
Advantages of Using Biogas
1. Renewable and Sustainable: Biogas is a renewable energy source that relies on the continuous availability of organic waste.
2. Waste Reduction: It provides an efficient way to manage organic waste, reducing landfill volumes and incineration needs.
3. Green Energy: Biogas significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels.
4. Economic Benefits: Biogas production creates jobs in waste collection, plant operation, and energy distribution.
5. Energy Security: It diversifies the energy mix and reduces dependence on non-renewable energy sources.
Conclusion
Biogas is a versatile and sustainable energy source with applications ranging from electricity generation and cooking to transportation and industrial processes. Its production promotes waste management and reduces greenhouse gas emissions, making it a vital component of the global shift toward renewable energy systems. By converting organic waste into valuable energy and fertilizer, biogas supports circular economy principles and offers a viable solution to some of the most pressing environmental challenges. As biogas technology continues to advance, its role in achieving sustainable development and energy independence will only grow.