The Distinction Unveiled: Cut vs. Copy
 In the realm of computer operations, two commonly used commands that often perplex users are “cut” and “copy”. These commands play a fundamental role in manipulating and managing digital content, allowing users to move or duplicate files, text, or other types of data. In this article, we will explore the key differences between “cut” and “copy”, shedding light on their respective functionalities and highlighting the diverse applications within the digital world.
In the realm of computer operations, two commonly used commands that often perplex users are “cut” and “copy”. These commands play a fundamental role in manipulating and managing digital content, allowing users to move or duplicate files, text, or other types of data. In this article, we will explore the key differences between “cut” and “copy”, shedding light on their respective functionalities and highlighting the diverse applications within the digital world.
Cut: Transferring Data with Precision
Understanding the “Cut” Command
The “Cut” command is a function that enables users to remove selected data from its original location and place it into a temporary storage known as the clipboard. This data can be in the form of files, folders, text, images, or any other type of digital content. Once the data is cut, it is no longer present at its original location, making it available for relocation or pasting elsewhere.
Key Features of the “Cut” Command:
- Removal of Data: When the “Cut” command is executed, the selected data is detached from its current location, leaving behind an empty space.
- Temporary Storage: The cut data is stored in the clipboard, a temporary holding area in the computer’s memory. This allows the user to move the data to a different location or paste it into another application.
- Moving Data: The primary purpose of the “Cut” command is to relocate the selected data to a new location. Once the data is pasted, it is removed from the clipboard, occupying the new destination.
- Keyboard Shortcut: The “Cut” command is often executed using the keyboard shortcut “Ctrl + X” (or “Command + X” on Mac computers), providing a quick and efficient way to initiate the operation.
Copy: Replicating Data for Diverse Applications
Understanding the “Copy” Command
The “Copy” command is a function that allows users to duplicate selected data without removing it from its original location. This data duplication is made possible by creating a copy of the selected content and storing it in the clipboard. The copied data can be subsequently pasted into the same or different location(s), providing versatility and flexibility in managing digital content.
Key Features of the “Copy” Command:
- Duplication of Data: The “Copy” command creates an exact replica of the selected data, leaving the original content intact in its original location.
- Temporary Storage: Similar to the “Cut” command, the copied data is also stored in the clipboard, allowing the user to paste it multiple times across different applications or locations.
- Versatile Usage: The copied data can be pasted into the same location or different locations, providing users with the ability to replicate content for various purposes.
- Keyboard Shortcut: The “Copy” command is commonly executed using the keyboard shortcut “Ctrl + C” (or “Command + C” on Mac computers), enabling users to swiftly duplicate data.
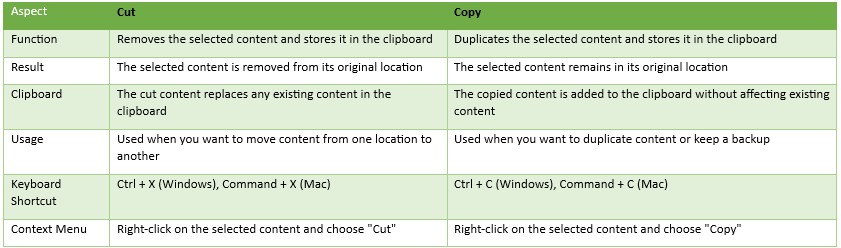
Here’s a table comparing the differences between Cut and Copy:
| Aspect | Cut | Copy |
| Function | Removes the selected content and stores it in the clipboard | Duplicates the selected content and stores it in the clipboard |
| Result | The selected content is removed from its original location | The selected content remains in its original location |
| Clipboard | The cut content replaces any existing content in the clipboard | The copied content is added to the clipboard without affecting existing content |
| Usage | Used when you want to move content from one location to another | Used when you want to duplicate content or keep a backup |
| Keyboard Shortcut | Ctrl + X (Windows), Command + X (Mac) | Ctrl + C (Windows), Command + C (Mac) |
| Context Menu | Right-click on the selected content and choose “Cut” | Right-click on the selected content and choose “Copy” |
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I cut or copy multiple files or folders at once?
Yes, you can cut or copy multiple files or folders simultaneously. Simply select all the desired files or folders and execute the “Cut” or “Copy” command accordingly.
2. Can I cut or copy text from one application and paste it into another?
Absolutely! The “Cut” or “Copy” command is not limited to specific applications. You can cut or copy text from one application and paste it into another, allowing seamless transfer of information.
3. Can I undo the “Cut” or “Copy” command?
No, once the “Cut” or “Copy” command is executed, it cannot be undone. Therefore, it is advised to exercise caution before initiating the operation to prevent accidental loss or duplication of data.
4. Can I cut or copy files between different storage devices?
Yes, you can cut or copy files between different storage devices as long as they are accessible from your computer. This includes transferring files between internal and external hard drives, USB flash drives, or network drives.
5. Do the “Cut” and “Copy” commands work the same way in all operating systems?
The “Cut” and “Copy” commands function similarly across different operating systems, such as Windows, macOS, and Linux. However, the keyboard shortcuts may vary slightly depending on the specific operating system.
Conclusion
The “Cut” and “Copy” commands are essential tools for managing and manipulating digital content. While the “Cut” command removes the selected data from its original location and places it in the clipboard for relocation, the “Copy” command duplicates the selected data while leaving the original content intact. Understanding the differences between “cut” and “copy” allows users to confidently perform file operations, ensuring efficient data management andorganization. Whether you need to move files to a new location or create duplicates for various purposes, mastering the concepts behind these commands is crucial in navigating the digital world effectively.
Remember, the “Cut” command is used when you want to remove data from its original location and relocate it, while the “Copy” command is employed to create replicas of data without removing the original content. Both commands offer their unique functionalities and can be accessed through keyboard shortcuts or menu options in most operating systems.
So, the next time you find yourself needing to manipulate digital content, whether it’s rearranging files or making copies, confidently choose between “cut” and “copy” based on your desired outcome. With a clear understanding of their distinctions, you’ll be able to wield these commands with precision and efficiency, streamlining your digital workflows.
Now that you have a grasp of the differences between “cut” and “copy,” feel free to explore the various applications and possibilities they offer. Harness the power of these commands to enhance your productivity and unleash the full potential of your digital endeavors.
Happy cutting and copying!