Decoding the Distinctions: Federation vs. Confederation
 Governments come in various forms, designed to establish and maintain order within a society. Two common types of government structures are federations and confederations. While both systems involve the sharing of power between multiple entities, they differ significantly in their organization, distribution of authority, and degree of centralization. In this article, we will delve into the disparities between federations and confederations, unraveling their unique characteristics and shedding light on their implications for governance.
Governments come in various forms, designed to establish and maintain order within a society. Two common types of government structures are federations and confederations. While both systems involve the sharing of power between multiple entities, they differ significantly in their organization, distribution of authority, and degree of centralization. In this article, we will delve into the disparities between federations and confederations, unraveling their unique characteristics and shedding light on their implications for governance.
Federation: The Unity in Diversity
What is a Federation?
A federation is a political system in which a central government coexists with regional or state governments, with each level possessing significant powers and responsibilities. In a federation, power is shared between the central authority and the constituent states or provinces. This system is often adopted by countries with diverse populations or regions seeking to maintain unity while preserving local autonomy.
Key Features of a Federation:
- Central Government: A federation has a central government that is responsible for the overall governance of the country. This central authority handles matters of national importance, such as defense, foreign affairs, and trade regulations.
- Regional or State Governments: In addition to the central government, a federation consists of regional or state governments. These entities have their own jurisdiction and authority over specific areas, such as education, healthcare, and transportation, as granted by the constitution or other governing documents.
- Division of Powers: Federations often establish a system of division of powers, where certain powers are assigned exclusively to the central government, while others are devolved to the regional or state governments. This division helps strike a balance between centralized authority and regional autonomy.
- Constitutional Framework: Federations are typically governed by a constitution that outlines the distribution of powers, rights, and responsibilities between the central government and the constituent states. This constitutional framework serves as the supreme law of the land, guiding the functioning of the federation.
Confederation: The Strength in Cooperation
What is a Confederation?
A confederation is a political system in which sovereign states or territories come together voluntarily to form a union based on mutual cooperation and shared interests. In a confederation, the central authority is relatively weak and dependent on the member states for its existence and power. This system is often adopted by nations or regions seeking to collaborate on specific issues while maintaining a high degree of sovereignty.
Key Features of a Confederation:
- Sovereign States: A confederation is composed of sovereign states or territories that retain their independence and self-governance. These states voluntarily enter into the confederation, pooling their resources and cooperating on matters of common interest.
- Limited Powers of the Central Authority: In a confederation, the central authority has limited powers, usually restricted to specific areas of common concern, such as defense, foreign affairs, and trade. The member states retain significant autonomy and have the power to make decisions on matters within their jurisdiction.
- Interstate Cooperation: The strength of a confederation lies in the cooperation and collaboration among the member states. Decisions are made through consensus or mutual agreement, and member states work together to achieve shared goals while respecting the sovereignty of each state.
- Loose Constitutional Framework: Unlike federations, confederations often have a loose constitutional framework that allows for flexibility and adaptability. The governing documents of a confederation outline the shared principles and objectives of the union but leave room for member states to determine their internal governance structures.
Differences between a federation and a confederation:
- Definition:
- Federation: A federation is a political system where power is divided between a central government and regional or state governments. The central government has authority over certain issues, while regional governments have their own areas of jurisdiction.
- Confederation: A confederation is a political system where independent states or regions come together and delegate limited powers to a central authority. In a confederation, the central authority’s power is derived from the member states, and the member states retain a significant level of sovereignty.
- Central Authority:
- Federation: In a federation, the central government has more power and authority compared to the regional governments. The central government can make decisions and enforce laws that apply to the entire federation.
- Confederation: In a confederation, the central authority has limited powers, and the member states have more autonomy. The central authority’s power is usually limited to areas like defense, foreign affairs, and trade.
- Sovereignty:
- Federation: In a federation, sovereignty is shared between the central government and the regional governments. The central government has sovereignty over matters that fall within its jurisdiction, while regional governments have sovereignty over matters within their respective regions.
- Confederation: In a confederation, member states retain their sovereignty and have the right to withdraw from the confederation if they choose to do so. The central authority’s power is derived from the consent and cooperation of the member states.
- Decision-Making:
- Federation: In a federation, decision-making is often a combination of centralized decision-making by the central government and decentralized decision-making by the regional governments. Power is shared, and decisions are made through a combination of cooperation and negotiation.
- Confederation: In a confederation, decision-making is primarily driven by consensus among the member states. The central authority relies on the agreement and cooperation of the member states to make decisions.
- Flexibility vs. Stability:
- Federation: Federations provide a balance between centralized authority and regional autonomy. They offer stability and a unified approach to certain issues while allowing for regional diversity and flexibility.
- Confederation: Confederations tend to be less centralized and offer more flexibility for member states. However, they may face challenges in coordinating actions and maintaining a unified approach due to the autonomy of the member states.
These are the key differences between a federation and a confederation. Each system has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them depends on the specific needs and circumstances of the countries or regions involved.
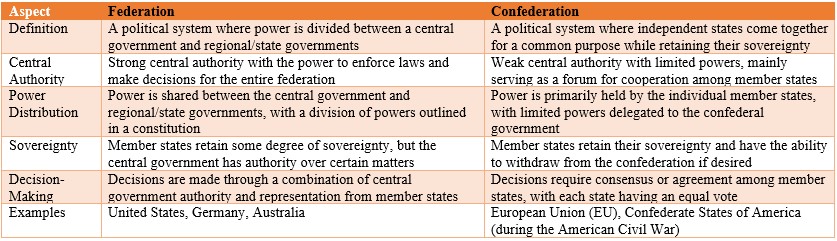
| Aspect | Federation | Confederation |
| Definition | A political system where power is divided between a central government and regional/state governments | A political system where independent states come together for a common purpose while retaining their sovereignty |
| Central Authority | Strong central authority with the power to enforce laws and make decisions for the entire federation | Weak central authority with limited powers, mainly serving as a forum for cooperation among member states |
| Power Distribution | Power is shared between the central government and regional/state governments, with a division of powers outlined in a constitution | Power is primarily held by the individual member states, with limited powers delegated to the confederal government |
| Sovereignty | Member states retain some degree of sovereignty, but the central government has authority over certain matters | Member states retain their sovereignty and have the ability to withdraw from the confederation if desired |
| Decision-Making | Decisions are made through a combination of central government authority and representation from member states | Decisions require consensus or agreement among member states, with each state having an equal vote |
| Examples | United States, Germany, Australia | European Union (EU), Confederate States of America (during the American Civil War) |
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the main difference between a federation and a confederation?
The main difference between a federation and a confederation lies in the distribution of power and the degree of centralization. In a federation, power is shared between the central government and the constituent states or provinces, with a stronger central authority. In a confederation, member states retain their sovereignty and voluntarily cooperate on specific issues, with a weaker central authority.
2. Can you provide an example of a federation?
One example of a federation is the United States of America. In the United States, power is divided between the federal government and individual states, with the Constitution outlining the distribution of powers and responsibilities.
3. Is the European Union a federation or a confederation?
The European Union (EU) can be considered a unique hybrid of both a federation and a confederation. While it has certain elements of a confederation, such as member states retaining their sovereignty, the EU also possesses aspects of a federation, such as a centralized legislative body and executive authority.
4. How does decision-making differ in a federation and a confederation?
In a federation, decision-making often involves a combination of centralized authority and input from regional or state governments. The central government may have the power to make decisions on matters of national importance, while regional or state governments have autonomy inmatters within their jurisdiction. In a confederation, decision-making is based on consensus among the member states, with each state having the power to veto or influence decisions that affect their sovereignty.
5. Can a federation evolve into a confederation, or vice versa?
While rare, it is possible for a federation to evolve into a confederation or vice versa. This transformation usually occurs due to significant changes in the political, social, or economic landscape of a country or region. It may involve a reevaluation of the distribution of powers, the weakening or strengthening of the central authority, or a shift in the relationship between the member states.
Conclusion: Embracing Diversity and Cooperation
In summary, federations and confederations are distinct forms of government structures that offer different approaches to governance. Federations promote unity while accommodating diversity, with a stronger central authority and shared powers between the central and regional governments. Confederations, on the other hand, emphasize cooperation among sovereign states while preserving a high degree of autonomy for each member. Both systems have their advantages and suit different contexts, demonstrating the importance of adapting governance structures to fit the needs and aspirations of a society. Understanding the differences between federations and confederations allows us to appreciate the nuances of governance and promotes informed discussions on the most effective models for ensuring stability and progress.
So, whether it is the strength of collaboration in a confederation or the unity in diversity of a federation, the key lies in embracing the variations and synergies that can lead to prosperous and harmonious societies.